Date:2025-05-30 Views:1023
Samarium cobalt magnets, also known as samarium cobalt magnetic steel, samarium cobalt permanent magnets, and rare earth cobalt permanent magnets, are made by blending samarium, cobalt, and other rare earth metals. They are processed through alloying, crushing, pressing, and sintering to form a magnetic material. This material features a high magnetic energy product, an extremely low temperature coefficient, and a maximum operating temperature of up to 350℃. It can function at temperatures below zero, and when the working temperature exceeds 180℃, its maximum magnetic energy product, as well as its temperature, chemical, and operational stability, surpass those of neodymium iron boron magnets. Samarium cobalt magnets also exhibit strong resistance to corrosion and oxidation, making them widely used in aerospace, microwave devices, communications, medical equipment, instruments, various magnetic drive devices, sensors, magnetic processors, motors, and magnetic cranes.
| Partial mechanical and physical properties of sintered samarium cobalt magnets | |||
| Parameter | Unit | Samarium cobalt 1:5 | Samarium cobalt 2:17 |
| Density D | G/cm3 | 8.3 | 8.4 |
| Curie temperature Tc | K | 1000 | 1100 |
| Vickers hardness Hv | MPa | 450-500 | 550-600 |
| Compressive strength δ c | MPa | 1000 | 800 |
| Electrical resistivity ρ | Ω.cm | 5~6×10-5 | 8~9×10-5 |
| Bending strength δ b | Mpa | 150-180 | 130-150 |
| Tensile strength δ t | Mpa | 40 | 35 |
| Thermal expansion coefficient α | (10-6/℃) | // 6⊥12 | // 8⊥11 |
Note: The above typical values are for reference only and cannot be used as a basis for material acceptance or rejection.
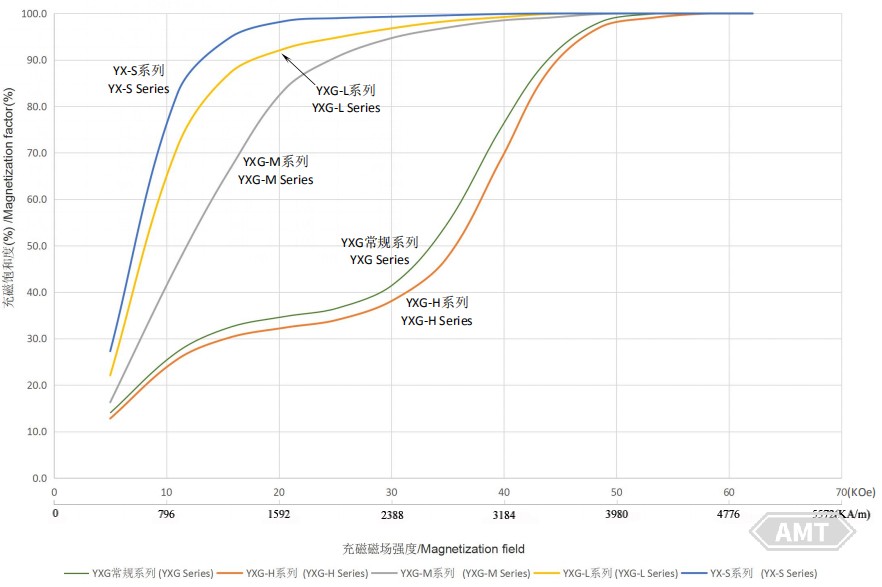
Note: Generally, the minimum required saturation magnetization magnetic field for sintering samarium cobalt 2:17 is 2-3 times the HCj value of the material itself.
| Comparison of Characteristics of Permanent Magnet Materials | |||||
| Material | Maximum magnetic product energy | Intrinsic coercivity | Br temperature system% ℃ number | Maximum operating temperature | Corrosion Resistance |
| Samarium cobalt 1:5 | 16-25 | 15-25 | -0.05 | 200-250 | better |
| Samarium cobalt 2:17 | 22-35 | 6-30 | -0.03 | 300-350 | better |
| Neodymium iron boron | 26-52 | 12-30 | -0.11 | 80-200 | poor |
| Ferrite | 3-4.5 | 3-4.5 | -0.19 | 200-300 | better |
| Aluminum nickel cobalt | 5-10 | 1-1.8 | -0.03 | 450-500 | better |
Sintered samarium cobalt magnets are brittle and not ductile, so they shouldn't be used as structural components in designs. SmCo1:5 has better mechanical and physical properties than SmCo2:17 and is slightly easier to process, while SmCo2:17 is more brittle. Handle magnetized samarium cobalt magnets carefully during assembly, avoid attracting them to ferrous materials to prevent breakage, and prevent collisions between magnets that could damage them or cause injuries.
Sintered samarium cobalt magnets may have minor appearance defects like chipped corners due to minor impacts during production, packaging, and transportation. These defects don't affect assembly, functionality, magnetic performance, stability, or demagnetization resistance.
Users requiring unmagnetized samarium cobalt magnets must know their magnetizing equipment's energy to select the right grade for full saturation.
For products used in acidic, alkaline, or harsh environments, we offer samarium cobalt magnets with electroplating of zinc, nickel, gold, or epoxy resin coatings. Thank you for using our samarium cobalt magnets. Feel free to contact us by fax or email for technical support. We're committed to providing high-quality and affordable samarium cobalt magnet products.
Leave your email for more ebooks and prices📫 !
Contact:Fidel
Tel:021-5512-8901
Mobile:19916725893
Email:sales7@atmsh.com
Address:No.398 Guiyang Road Yangpu China